Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Lehrstuhl für Medizinphysik, Fakultät für Physik, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Am Coulombwall 1, D-85748, Garching, Germany
2 Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, D-85748 Garching, Germany
3 Peking University, Beijing 100871, PR China
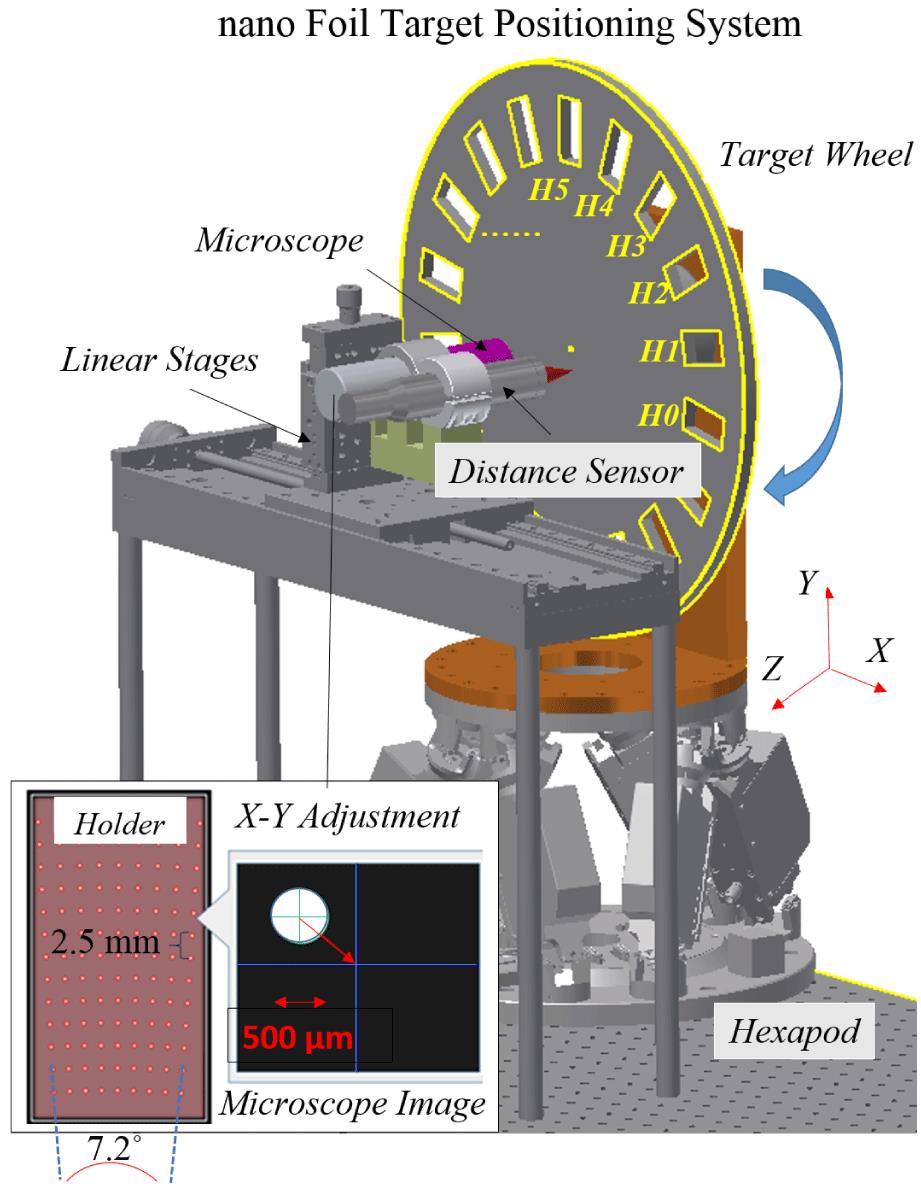
We report on a target system supporting automated positioning of nano-targets with a precision resolution of $4~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m}$ in three dimensions. It relies on a confocal distance sensor and a microscope. The system has been commissioned to position nanometer targets with 1 Hz repetition rate. Integrating our prototype into the table-top ATLAS 300 TW-laser system at the Laboratory for Extreme Photonics in Garching, we demonstrate the operation of a 0.5 Hz laser-driven proton source with a shot-to-shot variation of the maximum energy about 27% for a level of confidence of 0.95. The reason of laser shooting experiments operated at 0.5 Hz rather than 1 Hz is because the synchronization between the nano-foil target positioning system and the laser trigger needs to improve.
high intense laser nm thick target positioning system repetition rated laser-driven ion source High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2017, 5(2): 02000e12
中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
用二维particle-in-cell (PIC)粒子模拟程序研究了等离子体初始温度对强激光与物质相互作用过程中高能质子产生的影响。观察到不同的等离子体初始温度会影响靶前激波的形成时间, 进而影响质子产额。数值模拟显示当等离子体初始温度适度增大时可以得到更高的质子产额。
激光等离子体 高能质子 粒子模拟 等离子体温度 激波





